Durability
Stiffness, Stress, Strain, Deformation, Strength & Durability Simulation by means of Finite Element Analysis
Our portfolio covers the entire range of typical customer needs in relation to numerical structural analysis.
A highly experienced team of analysts provides related services.
Starting with support on the definition of analysis tasks (model size, boundary conditions, loads, methodology) followed by the exact and efficient calculation and report generation ending with the professional interpretation of the results and the derivation of practical design recommendations, we support our customers with advice and action.
By permantely improving our methods or new analytical approaches, we develop efficient simulation processes that will be used in internal developments, but also be offered to our "external" customers. Through our know-how, the close cooperation with the FEMFAT software development, the intensive cooperation with our test facilities as well as the exchange of experience with other simulation experts (within the company and with many well-known vehicle manufacturers and suppliers or mechanical engineering companies), we can optimally carry out simulation tasks.
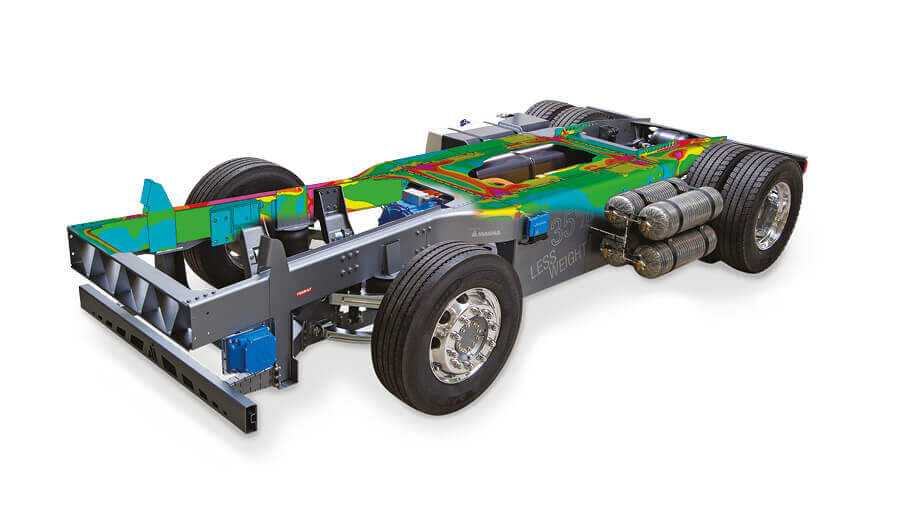
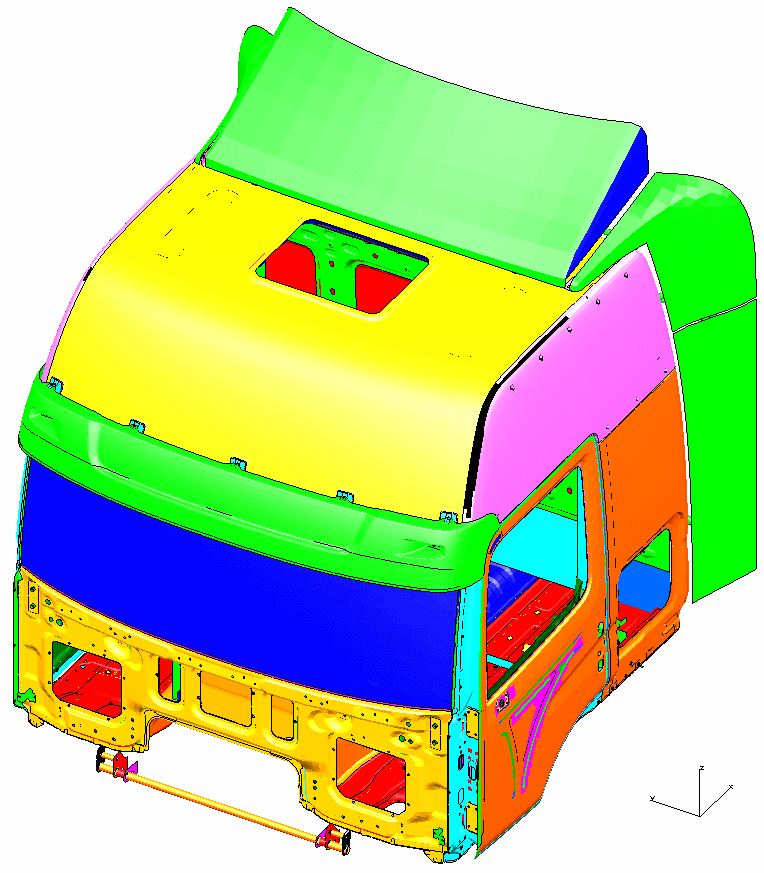
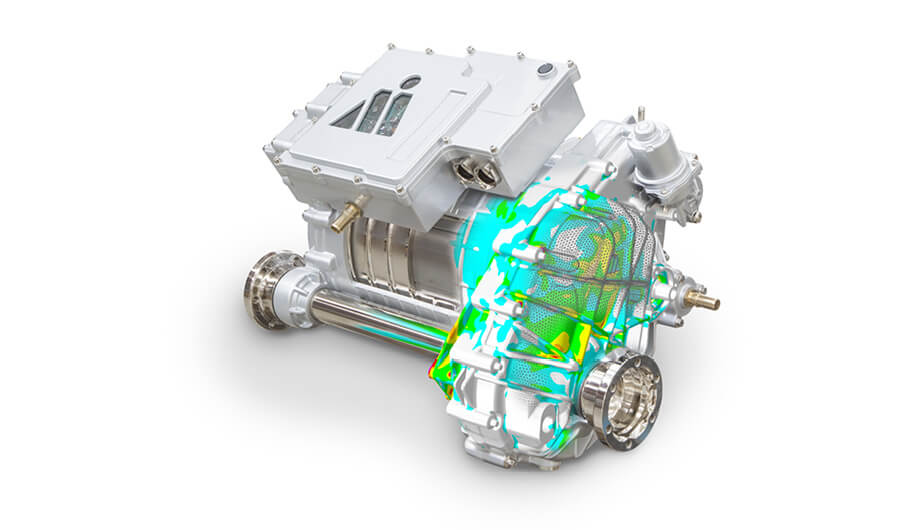
The long-serving employees of the fatigue strength simulation, with an average experience of 16 years, are divided into 3 teams. The activities focus on calculations in the area of powertrains (ICE, e-motors, inverters, transmissions), frames and chassis parts as well as on bodies, cabins and vehicle substructures. In addition to these main focal points, with extensive experience from a large number of projects for passenger cars (cars), commercial vehicles (trucks), construction and agricultural vehicles as well as special vehicles, we also support our customers in the areas of rail vehicles (bogie or car body) or classic mechanical engineering.
Depending on the project phase, different model and analysis depths are offered. This meets the relevant requirements in terms of timeline and available budget. The spectrum ranges from a quick concept study to an intensive study of detailed effects.
For our different customers we offer these calculations using different commercial tools, depending on the wishes or strengths of the individual software packages. ANSA, HYPERWORKS and ANSYS are used as pre- and post-processors. The Finite Element calculations are carried out with ABAQUS (usually for non-linear problems), NASTRAN (usually for linear calculations) or, if requested by the customer, with ANSYS. For fibre-reinforced, anisotropic plastic components, we can also carry out an injection molding simulation using MOLDEX3D in combination with DIGIMAT in order to be able to include the fiber orientation in the FE model.
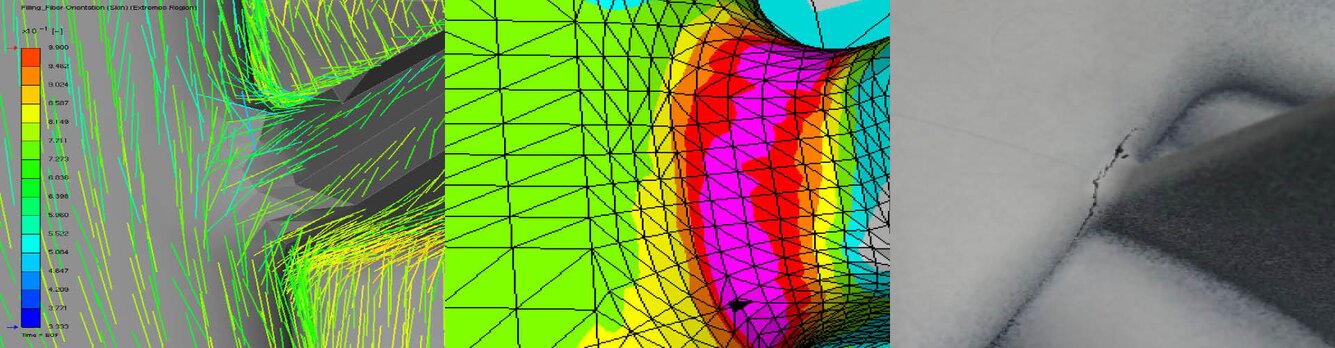
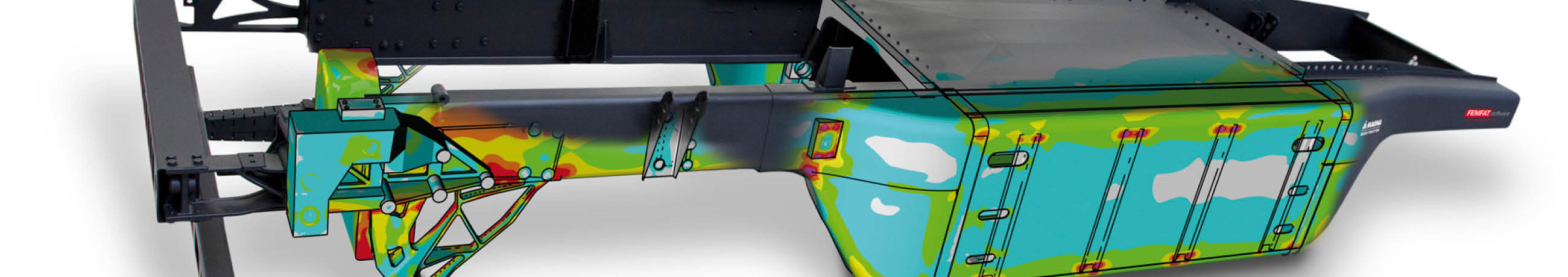
Beside typical results of such Finite Element analyses like stiffness, deformation, stress and strain additional information, such as detailed information regarding the contact behavior of two components (e.g. lifting) or whether a relative movement of two structures is expected, can be derived.
Subsequent to the Finite Element analysis (FEA), the structures are usually assessed with regard to durability. This evaluation is carried out using the FEMFAT software package developed in the ECS. I.e. in addition to almost all common base materials, the connection techniques commonly used in vehicle construction (spot weldings, arc weldings, self piercing rivets, adhesives, FDS, ...) can also be evaluated. Analyzes can be carried out for static strength cycles as well as for finite and infinite life range (HCF). Likewise, thermo-mechanical fatigue (TMF) of hot components can be calculated. Since FEMFAT is also used by many of our customers as durability software for development of products we offer base material tests and strength tests of various connection technologies and the corresponding adaptation of the FEMFAT databases, together with the strength laboratory of the ECS or with suitable external partners, as a service for our customers.
In addition to the classical component improvement by iterative simulations of improved structures, our customers also have the option of numerical optimization. During topology optimization, starting from a maximum design space, the geometry is reduced to such an extent that the material is stressed as uniformly as possible (TOSCA software) when a target mass is specified. Such optimizations can be stress-based (uniform stresses) or damage-based (damage distribution as uniform as possible). By parameter optimization with HYPERSTUDY or ISIGHT, mostly local design features are adapted in order to improve the design.
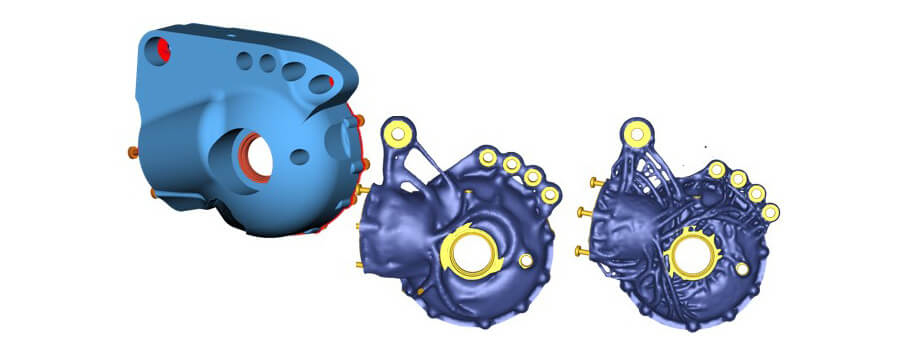
Typical investigations of our individual teams are